NEC: Demonstration of Secure Data Backup of Medical Records Using Secret Sharing on Secure Communications Network
- Written by ACN Newswire - Press Releases

|
|
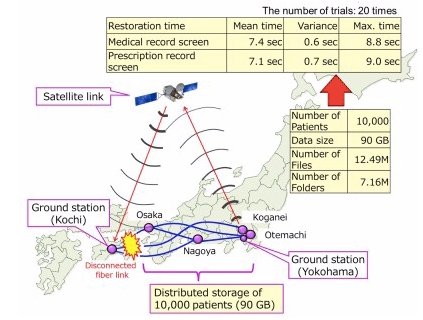
| Figure 1: Network configuration of H-LINCOS and experimental results |
Background
In the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011, many medical institutions were destroyed and data servers storing medical records were washed away by tsunami waters. It was then recognized that medical records should be backed up in remote places safely for such contingencies. In the case of emergency care after a disaster, medical examinations and treatment should be given to many people in a short time. During these times, there is a need to promptly restore a minimum of necessary items to profile a patient, such as prescription records and allergy information.
Medical records are highly confidential personal information. Therefore, the backup of medical records should be protected by appropriate security techniques. Furthermore, if the backup conforms to a common standardized data format, they can be shared and cross-referenced by many medical institutions to prevent duplicated examination and excessive medication as well as to develop new medical technologies.
So far, no techniques have been available which satisfy all these requirements at once.
Achievements
We combined secret sharing and secure communications technologies to realize a secure data backup system and demonstrated distributed storage of medical records and prompt restoration of important items, such as prescription records and allergy information, via a satellite link. This system is referred to as the Healthcare Long-term INtegrity and Confidentiality protection System (H-LINCOS). This H-LINCOS has been implemented in an 800 km network connecting the data servers in KHSC, and the access points of a high-speed R&D network testbed called JGN operated by NICT, which are located in Osaka, Nagoya, Otemachi, and Koganei (see Figure 1. An enlarged version is also shown in the end of appendix.). To realize highly secure access control to the H-LINCOS, authentication functions are also implemented, using next generation technologies of quantum-safe public-key cryptography, which is expected to be secure even against quantum computer attacks.
In this experiment, sample data of medical records of 10,000 patients were provided by KHSC, whose total data size was 90 GB, converted into the standardized data format for medical information exchange (SS-MIX)(3), and stored in a distributed manner in the H-LINCOS. In the demonstration of data recovery, we assumed that the Kochi area was damaged by a disaster, and terrestrial communication links to the Kochi area were disconnected. Under this scenario, a satellite link provided by SKY Perfect JSAT was introduced to the H-LINCOS connecting the ground stations in Yokohama and KHSC. Upon a query for a patient data item from a terminal device in KHSC, the original data was first restored in the Koganei data server by combining data pieces from two data servers in Osaka, Nagoya or Otemachi. The restored data was then sent to the Yokohama ground station, relayed to the KHSC ground station via the satellite link, and finally delivered to the terminal device in KHSC.
We could successfully restore important items, such as prescription records and allergy information, and display them on a screen within a time as short as 9 sec after the query. An allowable time to wait for information acquisition in emergency medicine is typically 15 sec. Our result satisfied this criterion. Our technology enables prompt delivery of medical information in disaster situations. It also provides a means to share and cross-reference medical records between various hospitals in ordinary situations.
Future Prospects
We will further improve the performance and the reliability of the H-LINCOS. In particular, we will analyze communication latencies and H-LINCOS congestion when the stored data size and the number of connected terminal devices to access increase. We will also investigate efficient healthcare support in disaster situations by jointly operating the H-LINCOS and the Disaster/Digital information system for Health and well-being (D24H)(4).
Publication of our results
Our results will be presented in the session of quantum communication on December 16 in the EU-USA-Japan International Symposium on Quantum Technology 2019 held in Kyoto.Title: Quantum enhanced communication and cryptographySpeaker: Masahide Sasaki (NICT)URL: https://bit.ly/2EcqNDG
Roles and tasks of our team members
- NICT: Grand design and implementation of H-LINCOS, conducting the experiment and managing the project- Kochi Health Science Center: Derivation of requirements for H-LINCOS and providing sample data of medical records- Kochi University of Technology: Derivation of requirements for H-LINCOS and design of secret sharing scheme- ZenmuTech: Development of fast secret sharing driver software- Shibaura Institute of Technology: Optimization of H-LINCOS for disaster medical support via D24H- SBS Information Systems Co., Ltd: Development of medical record viewer- SKY Perfect JSAT Corporation: Providing a satellite link- NEC Corporation: Implementation of secure communication channels between the KHSC and Koganei access points- ISARA Corporation: Development of quantum-safe public-key infrastructure for healthcareTechnische Universit?t Darmstadt: Development of long-term secure integrity protection scheme
Glossary
(1) secret sharingTechnique to create new multiple (say n) data (shares), each of which is of no use on its own, from an original data, and store the shares in different storage servers (shareholders) in a distributed manner. In a (k, n)-threshold scheme, the original data is restored by collecting at least k (≤n) of shares. With shares of k-1 or less, the original data can never be reconstructed, even with unlimited computing power. Provided that the number of corrupted shareholders is less than k, and shares are exchanged through private channels, the (k, n)-threshold scheme ensures information theoretic confidentiality of storage. Even if shares up to n- k are lost, the original data can be reconstructed by using the k remaining shares, which provides availability of data.(2) secure communication technologyTechnique to protect the confidentiality of transmitted data by using appropriate cryptographic methods. Symmetric key ciphers are commonly used at present. This scheme is, however, threatened by advances of computing technology. Recently quantum cryptography has become available, which can remain secure even against any computing technologies, ensuring information theoretical security.(3) SS-MIX: Standardized Structured Medical Information eXchangeStandardized data storage structure for exchanging medical information between medical institutions specified by the program called Standardized Structured Medical Information eXchange (SS-MIX) by Japan?s the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare. The SS-MIX data format is based on hierarchical folder structure based on patient ID.(4) disaster/Digital information system for Health and well-being (D24H)A system to provide necessary information for decision making on disaster healthcare support by gathering, integrating, and analyzing various information from the Shared Information Platform for Disaster Management (SIP4D) system managed by Ministries and individual systems operated by rescue teams and medical support teams.
Acknowledgements
A part of this work was performed by the Council for Science, Technology and Innovation (CSTI), the Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP), the ?Photonics and Quantum Technology for Society 5.0? (Funding agency: QST) and ?Enhancement of National Resilience against Natural Disasters? (Funding agency: NIED).
About NEC Corporation
NEC Corporation is a leader in the integration of IT and network technologies that benefit businesses and people around the world. The NEC Group globally provides "Solutions for Society" that promote the safety, security, efficiency, and equality of society. Under the company's corporate message of "Orchestrating a brighter world," NEC aims to help solve a wide range of challenging issues and to create new social value for the changing world of tomorrow. For more information, visit NEC at https://www.nec.com.
Contact:NEC Seiichiro Toda s-toda@cj.jp.nec.com +81-3-3798-6511
Copyright 2019 JCN Newswire. All rights reserved. www.jcnnewswire.com
Authors: ACN Newswire - Press Releases
Read more //?#